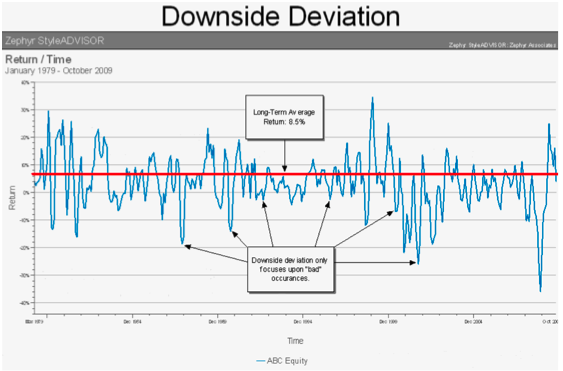
A vulnerability to events that impact broad economic outcomes is called systematic risk. These outcomes include aggregate income, total resource holdings, and market returns. Therefore, the level of systematic risk in a country can vary greatly. There are three types of systemic risk. These are: market risk, inflation and negative externalities. Let's go over each one. Consider how systematic threats affect your investments, and your portfolio.
Market risk
Investors who invest in stocks or bonds face systemic risk. Also known as market risk. This is due to changes in the prices of the underlying assets and the underlying markets. In the financial markets, this risk is often exacerbated by large investors holding large amounts of securities. Investors face market risk as well as credit and other risks. This refers to uncertainty regarding a company’s prospects, credit worthiness, or ability to repay debt.
Inflation risk
Inflation can be a serious risk to a person's financial security. It reduces the purchasing power of money as prices rise over time. Fixed income investments like bonds have high purchasing power and are subject to inflation. Bonds, for example, generally have a fixed rate of interest. There are many financial tools that investors have access to to reduce the risk of inflation. Here are some. -Inflation periods are a good time to increase your income in order to reduce systematic risk
Purchasing power risk
The systematic risk of purchasing power loss, also known by inflation risk, can result in your investment portfolio losing value over time. This is due to inflation, which reduces the money's purchasing power. This means that the same amount money can buy fewer goods and services. This can make your spending more difficult. Purchasing power risk is particularly problematic for fixed income securities, since these investments are valued in nominal terms. Equity shares, however, are less susceptible to purchasing power risks.
Negative externalities
There are many examples of negative externalities in economics. Light pollution is an example. When street lights are turned on, they affect the surrounding neighborhoods, but there's no way to compensate those affected. Other examples include environmental impacts of production or consumption. One example is that the cost of manufacturing products can create noise that is disruptive to nearby residents. Consumers don't have to compensate for this noise. The environmental effects of production and consumption can be a significant source of negative externalities.
Increasing capital
There is a positive correlation between a firm's risk capital and expected returns. But, if the risk capital required is too low, the correlation is negative. This is because bank stocks can be undervalued by capital requirements. These effects can't be avoided. It is important for policymakers to consider other policies in addition to increasing capital requirements to avoid such negative effects. This paper examines the main options for policy.
Diversification
Diversification, as its name suggests, can help you manage both systematic risk and unsystematic. Systematic risk is an undistributed risk in the stock market. Unsystematic risks can affect all markets, but systematic risk is only limited to one security or portfolio. Diversifying your portfolio is the best way minimize systematic risk. Diversification reduces the risk of systematic failure by narrowing possible outcomes and increasing portfolio diversity.

Measurement
Systematic risk refers to the possibility of financial system failures due the system's characteristics. Due to its enormous costs, it is imperative that financial institutions are properly regulated macroprudentially. This paper presents a novel approach to measure systemic risk. This analysis will prove to be very useful for policymakers wishing to preserve the stability and minimize the costs of the financial sector. The methodology is based in statistical methods and can apply to any type or financial system.
FAQ
Why is project management important for companies?
Project management techniques are used to ensure that projects run smoothly and meet deadlines.
Because most businesses depend heavily on project work to produce goods or services,
Companies must manage these projects effectively and efficiently.
Companies may lose their reputation, time and money if they do not have effective project management.
What are the top management skills?
Any business owner needs to be able to manage people, finances, resources and time. They are the ability to manage people and finances, space, money, and other factors.
Management Skills are also needed when you're setting goals and objectives, planning strategies, leading teams, motivating employees, resolving problems, creating policies and procedures, and managing change.
There are so many managerial tasks!
How does Six Sigma function?
Six Sigma uses statistical analysis for problems to be found, measured, analyzed root causes, corrected, and learned from.
First, identify the problem.
The next step is to collect data and analyze it in order to identify trends or patterns.
The problem is then rectified.
Finally, data will be reanalyzed to determine if there is an issue.
This continues until you solve the problem.
What is TQM and how can it help you?
The industrial revolution saw the realization that prices alone were not sufficient to sustain manufacturing companies. This led to the birth of quality. They needed to improve the quality and efficiency of their products if they were to be competitive.
Management developed Total Quality Management to address the need for improvement. It focused on all aspects of an organisation's performance. It included continual improvement processes, employee involvement, customer satisfaction, and customer satisfaction.
Statistics
- Our program is 100% engineered for your success. (online.uc.edu)
- Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees (upcounsel.com)
- As of 2020, personal bankers or tellers make an average of $32,620 per year, according to the BLS. (wgu.edu)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
External Links
How To
How can you apply the 5S in the office?
Your first step in making your workplace more efficient and productive is to organize everything. A clean desk, a neat room, and a well-organized space are all key factors in ensuring everyone is productive. The five S’s (Sort. Shine. Sweep. Separate. and Store) all work together to ensure that every inch is utilized efficiently and effectively. This session will take you through each step and show you how they can fit into any environment.
-
Sort. Clear away clutter and paper so that you don’t spend time looking for it. This means you place items where you will use them the most. It is a good idea to keep things near where you are most likely to refer to it. You need to think about whether or not you really have to keep it around.
-
Shine. Keep your belongings tidy and organized so you can spend less time cleaning up afterwards. Don't leave anything that could damage or cause harm to others. For example, if you have a lot of pens lying around, find a way to store them safely. A pen holder is a great investment as you won't lose your pens.
-
Sweep. Regularly clean surfaces to keep dirt from building up on furniture and other household items. To ensure that surfaces are clean and as neat as possible, you might consider investing in dusting equipment. To keep your workspace tidy, you could even designate a particular area for dusting and cleaning.
-
Separate. Separating your trash into different bins will save you time when you need to dispose of it. Trash cans are usually placed strategically throughout the office so that you can easily throw out the garbage without searching for it. To make sure you use this space, place trash bags next each bin. This will save you the time of digging through trash piles to find what your looking for.